
Lynnhan – əvansıdxalı Təchizatçı | LED/OLED/LCD/E-paper digital signages
Lynnhan – əvansıdxalı Təchizatçı | LED/OLED/LCD/E-paper digital signages

Lynnhan – əvansıdxalı Təchizatçı | LED/OLED/LCD/E-paper digital signages
Lynnhan – əvansıdxalı Təchizatçı | LED/OLED/LCD/E-paper digital signages

What is an OLED Display? A Comprehensive Guide by Lynnhan
1. Տեսահաղորդական տեխնոլոգիայի աշխարհում, OLED (օրգանական լուսանակալ դիոդ) դարձել է խաղափոփոխիչ։ Անվանի գերազանց պատկերագրությամբ, մեծ պլաստիկությամբ և էներգաէֆիկուենցիայով, OLED ցուցադրիչները հեղափոխում են արտադրանքային էլեկտրոնային սարքերից մինչև տաճառային արտադրանքներ արդյունաբերությունները։ Լիննհան.com-ում, մտադրության ապրանքանոց մեր հավատարման, մենք այստեղ ենք ներկայացնում որ են OLED ցուցադրիչները, ինչպե՞ս են նրանք աշխատում, և ինչու են նրանք այնքան բարձր գնահատվում։
2. Որբանգ OLED ցուցադրիչ?
3. OLED ցուցադրիչը տեսահաղորդական տեխնոլոգիա է, որ օգտագործում է օրգանական մ
How Does an OLED Display Work?
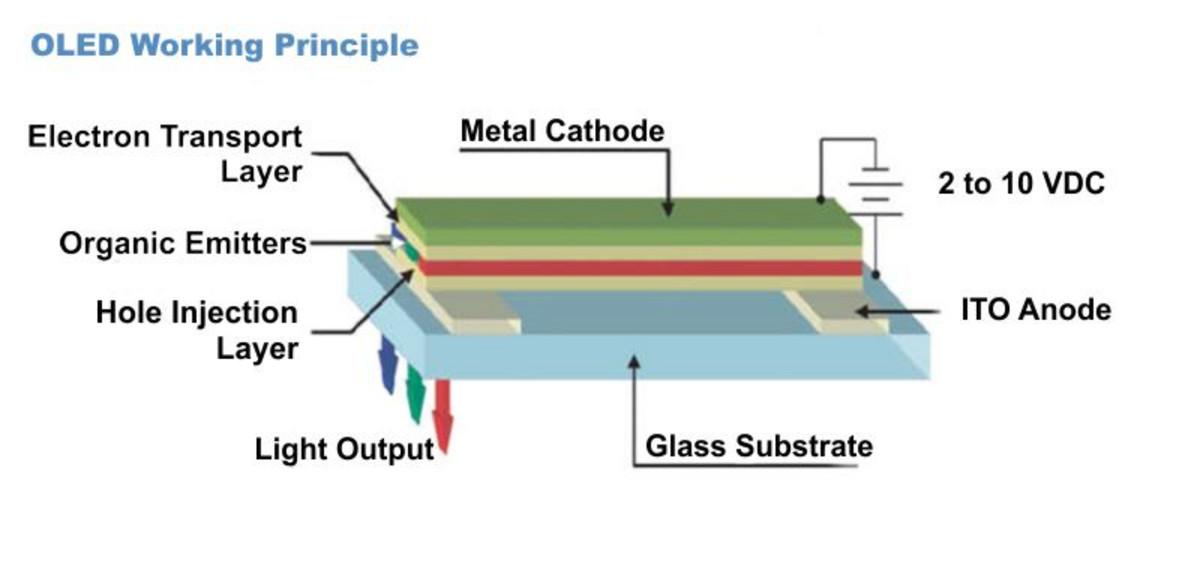
OLED displays are made up of thin layers of organic materials sandwiched between two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When electricity is applied, the organic compounds emit light. The basic structure of an OLED display includes:
- Substrate: The base layer, usually made of glass or plastic, that supports the OLED structure.
- Anode: A transparent layer that removes electrons when a current is applied.
- Organic Layers: These include the emissive layer (which emits light) and the conductive layer (which transports electrons).
- Cathode: A reflective layer that injects electrons into the organic layers.
When voltage is applied, electrons flow from the cathode to the anode, passing through the organic layers. This process excites the organic molecules, causing them to emit light. By controlling the intensity of the light emitted by each pixel, OLED displays can produce a wide range of colors and shades.
Types of OLED Displays
At Lynnhan.com, we offer a variety of OLED displays to meet different needs. Here are the most common types:
- Passive-Matrix OLED (PMOLED)
PMOLED displays are simpler in design and are typically used in smaller devices like smartwatches and MP3 players. They are cost-effective but have limitations in terms of resolution and screen size. - Active-Matrix OLED (AMOLED)
AMOLED displays are more advanced and are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and TVs. They use a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane to control each pixel individually, resulting in higher resolution, faster response times, and better energy efficiency. - Flexible OLED
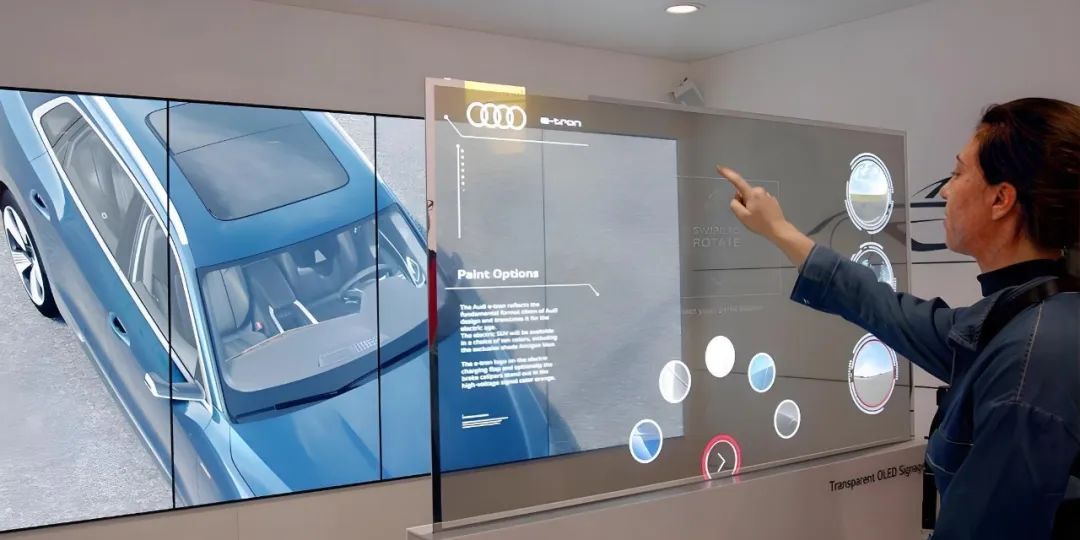
Flexible OLED displays are made using plastic substrates instead of glass, allowing them to bend or fold. These displays are used in innovative applications like foldable smartphones and curved TVs. - Transparent OLED
Transparent OLED displays allow light to pass through the screen, making them ideal for augmented reality (AR) applications, retail displays, and smart windows. - Top-Emitting OLED
These displays emit light from the top of the structure, making them more efficient and suitable for high-resolution applications like microdisplays.
Benefits of OLED Displays
OLED displays offer several advantages over traditional display technologies like LED and LCD. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Perfect Blacks and Infinite Contrast
Since each pixel emits its own light, OLED displays can completely turn off individual pixels to achieve true blacks. This results in an infinite contrast ratio, providing a more immersive viewing experience. - Durability and Longevity
OLED显示器即使在极端角度观看也能保持一致的色彩和亮度,这使得它们非常适合群体观看。 - 薄型轻便设计
OLED显示器不需要背光,这使得它们可以非常薄且轻便。这使得它们非常适合时尚现代的设备。 - sustainable choice
OLED显示器功耗更低,尤其是在显示较暗的内容时,因为单个像素可以完全关闭。 - 快速响应时间
与LCD相比,OLED显示器的响应时间更快,减少了运动模糊,使它们非常适合游戏和快速内容。 - 生动色彩
OLED显示器提供更宽的色域,产生更生动逼真的图像。
OLED显示器的应用
由于其卓越的性能和多功能性,OLED显示器被广泛应用于各个行业。以下是一些最常见的应用:
- Where do you see the next breakthrough in LED displays? Let’s discuss! OLED显示器广泛应用于智能手机、平板电脑、笔记本电脑和电视,提供令人惊叹的视觉和简洁的设计。
- 可穿戴设备: 智能手表和健身追踪器使用OLED显示器,因为它们节能且灵活。
- 汽车行业: OLED显示器用于汽车仪表盘、信息娱乐系统和后排娱乐屏幕。
- Advertising: 数字标牌和零售显示器得益于OLED鲜艳的色彩和薄型设计。
- 医疗设备: 由于其高分辨率和准确性,OLED显示器用于医疗成像和诊断设备。
- 增强现实(AR): 透明OLED显示器非常适合AR应用,提供数字和真实世界内容的无缝融合。
OLED与LED/LCD显示器比较
虽然OLED显示器提供了许多优点,但了解它们与传统LED和LCD显示器的比较是很重要的:
- 黑色水平: OLED显示器可以实现完美的黑色,而LED/LCD显示器则依赖于背光,这可能导致光渗。
- 观看角度: OLED显示器在宽角度下保持一致的色彩,而LED/LCD显示器可能会出现色彩偏移。
- 厚度: 由于没有背光,OLED显示器更薄更轻。
- 寿命: LED/LCD显示器通常具有更长的寿命,因为OLED显示器可能会随着时间的推移出现烧屏现象。
- Cost: OLED显示器通常比LED/LCD显示器更贵,尽管价格正在逐渐降低。
为什么选择Lynnhan.com满足您的OLED显示器需求?
在Lynnhan.com,我们致力于提供满足客户需求的高质量OLED显示器。以下是您选择我们的原因:
- Wide Range of Products: 我们提供多样化的OLED显示器选择,包括灵活和透明选项。
- Superior Quality: Our products are sourced from reputable manufacturers and undergo rigorous quality checks.
- Expert Support: Our team of experts is always ready to assist you in choosing the right display for your application.
- Competitive Pricing: We provide affordable solutions without compromising on quality.
- Global Shipping: No matter where you are, we deliver our products worldwide.
At
OLED显示器代表着显示技术的巅峰,提供无与伦比的画质、能源效率和设计灵活性。无论您是寻找高端电视、前沿智能手机还是创新广告解决方案,OLED显示器都能提供卓越的性能。
今天探索我们的收藏品,发现满足您需求的完美OLED显示器。
For more information or to place an order, visit Lynnhan.com让我们帮助您通过OLED体验显示技术的未来!